20 Weird Food Questions You Didn’t Know You Had

Ever wondered about the mysteries behind your favorite snacks and meals? This article dives into quirky and unexpected food questions that will tickle your curiosity.
From why pineapple makes your tongue tingle to the mystery of blue raspberry flavor, these questions will have you pondering your next bite.
Prepare to be surprised by questions you never thought to ask about everyday foods!
1. Why Doesn’t Cheese Melt The Same Way Every Time?

Different cheeses behave uniquely under heat because of their composition. Moisture, fat content, and acidity all determine how they react in the pan. Soft cheeses like Brie or mozzarella melt easily and become stretchy or creamy. Aged cheeses such as Parmesan or Romano tend to resist melting due to protein density and low moisture.
The way cheese is processed also matters—a block may melt better than a pre-shredded version coated in anti-caking agents. Even how long it’s been refrigerated can change the melt. What looks like magic is actually a delicate chemical ballet.
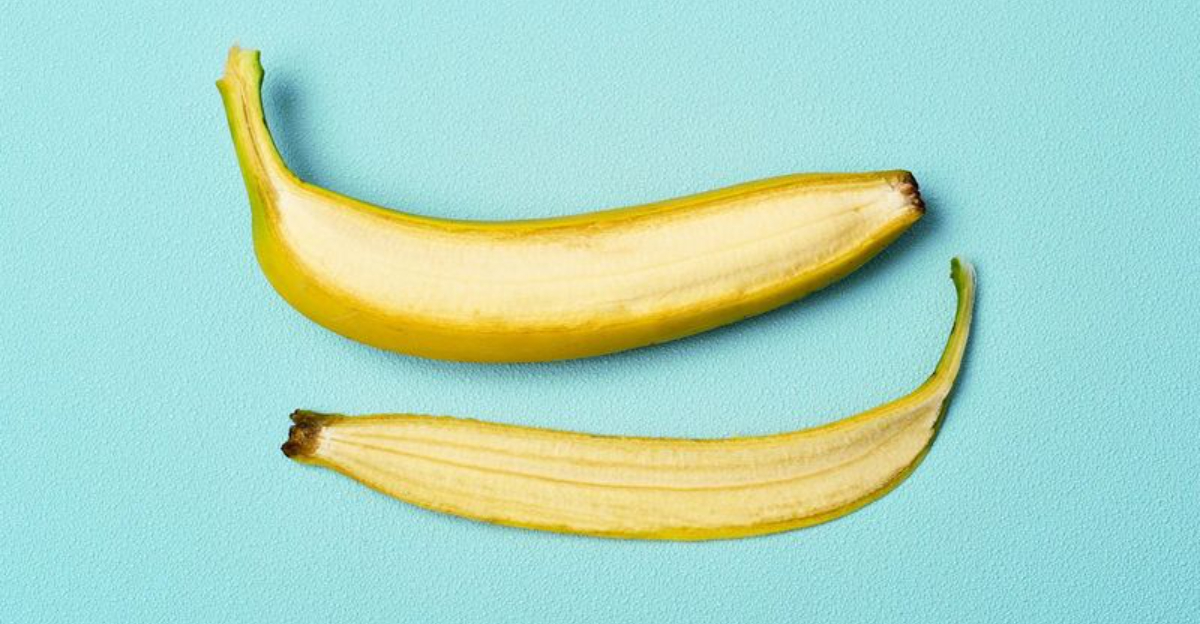
2. Can You Eat Banana Peels?
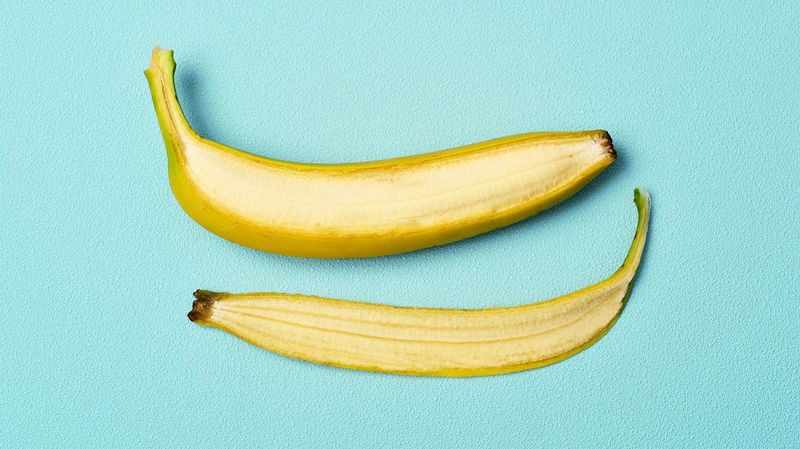

Yes, banana peels are technically edible and eaten in several cultures around the world. They’re full of fiber, potassium, and antioxidants. The texture is rubbery and the taste is bitter when raw, so most people avoid them.
However, cooking them softens the peel and improves the flavor, especially when stir-fried or blended. Indian and Filipino dishes sometimes feature banana peel as a meat substitute or savory side. Just wash thoroughly, especially with conventional bananas that may carry pesticide residue.
3. What’s Really In “Natural Flavors”?

“Natural flavors” sound wholesome but are often anything but simple. Legally, the base must come from a plant or animal source—like fruit, vegetables, meat, seafood, herbs, or spices. But after that, it goes through intense lab processing to isolate, stabilize, and enhance specific taste compounds.
Dozens of synthetic additives might be used in the process, even though the origin is natural. Two “natural” lemon flavors could be made with entirely different ingredients. The label reveals almost nothing about what you’re actually tasting.
4. Why Does Pineapple Make Your Mouth Feel Weird?
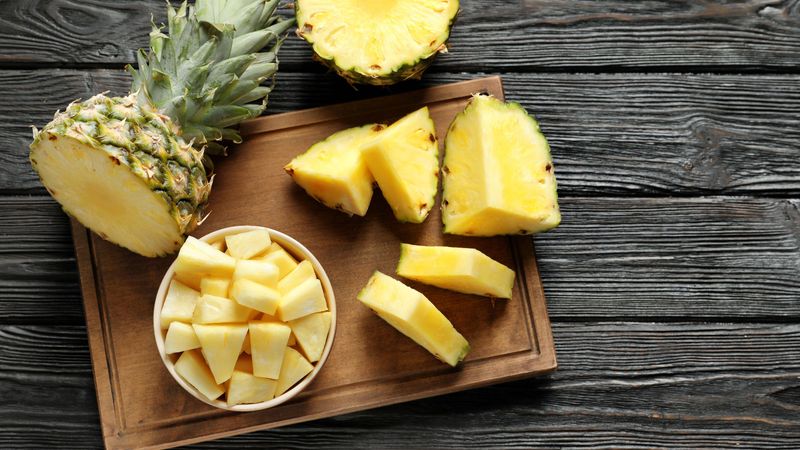

That sting on your tongue after pineapple isn’t your imagination. Pineapple contains bromelain, an enzyme that breaks down protein—including the proteins in your mouth. As you chew, the enzyme begins to tenderize your tongue’s surface.
It creates a prickling, sore sensation, especially with large amounts of raw pineapple. The effect wears off quickly and isn’t harmful. Cooking or canning the pineapple neutralizes bromelain, which is why grilled or baked versions don’t bite back.
5. Is It Safe To Eat Food After The Expiration Date?

That date stamped on the label is usually about quality, not safety. Many dry or canned foods are still perfectly edible after the printed date. For perishables like milk or meat, trust your senses—look, smell, and texture often reveal more than a number.
Of course, if it’s moldy or smells off, toss it immediately. Expired food doesn’t turn toxic at midnight. However, with vulnerable immune systems or high-risk items, playing it safe matters.
6. Why Does Mint Taste Cold?

Mint contains menthol, a compound that tricks your nervous system. Menthol binds to the same receptors in your mouth that detect cold temperatures. The result is a cooling sensation even when the food is room temperature or warm.
This trickery is purely sensory, your mouth doesn’t actually change temperature. That’s why mint makes gum or toothpaste feel icy, even when you’re not sipping anything cold. It’s a flavorful illusion created by molecules and nerves.
7. Can You Cook An Egg On A Sidewalk?
It’s a favorite myth, but the reality is less appetizing. Egg whites solidify at about 158°F, and most sidewalks max out around 130°F on even the hottest days. While the pavement might feel sizzling to the touch, it won’t reliably cook an egg.
You’ll end up with a gooey, half-cooked mess that’s more art than omelet. A metal surface, like a black car hood, might get closer to cooking temp. Still, you’re better off using a pan.
8. Why Does Ketchup Take Forever To Pour, Then Suddenly Gush Out?

Ketchup behaves like a non-Newtonian fluid, meaning its flow changes with pressure. At rest, it’s thick and resistant; when shaken or squeezed, it suddenly loosens. This is why tipping the bottle seems useless until—whoosh—it explodes everywhere.
The viscosity shifts once enough force is applied. Tapping the “57” on a glass Heinz bottle isn’t a myth—it helps release the flow slowly. Squeeze too hard, and your fries disappear under a tomato flood.
9. Are Baby Carrots Actually Baby-Sized?

Most of the baby carrots sold in stores aren’t small by nature. They’re carved down from full-sized carrots to be uniform and snack-ready. The process involves peeling, trimming, and shaping them into small stubs.
Originally developed to reduce food waste, this method repurposes imperfect carrots. Real baby carrots—harvested young and tender—do exist but are rarely seen in supermarkets. What you’re eating is a sculpted illusion.
10. Why Does Cereal Taste Better At Night?

There’s something magical about nighttime snacking. Your taste buds may be more responsive after a day of neutral meals. Sweetness also feels more comforting when the body is tired.
Cereal combines sugar, crunch, and milk—making it nostalgic and satisfying. Some say it’s psychological, others call it habit. Either way, nighttime cereal hits differently.
11. What Gives Blue Raspberry Its Flavor?

Blue raspberry is a made-up flavor created to stand out from red-colored sweets like cherry or strawberry. It combines notes of banana, cherry, and citrus to create a tangy, electric taste. The vivid blue dye was added purely for marketing.
There’s no blue raspberry in nature—it’s based loosely on the whitebark raspberry, which is more purple than blue. The flavor was designed in labs, not orchards.
12. Can Hot Sauce Actually Burn Your Tongue?
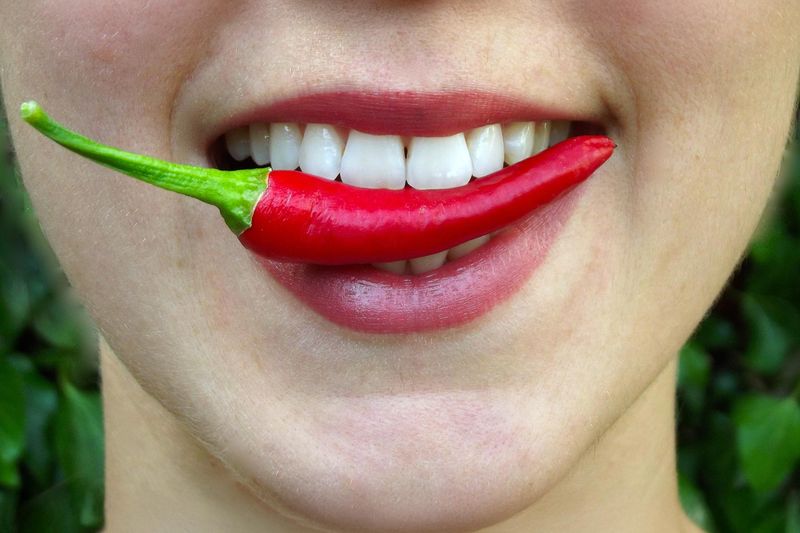

Hot sauce doesn’t cause literal burns, but the sensation feels real. Capsaicin binds to pain receptors meant to detect heat, making your brain think you’re on fire. That’s why even a tiny dab can make your mouth feel like it’s boiling.
The intensity depends on the Scoville level. It’s not dangerous in small doses, but too much can cause irritation, sweating, or even nausea. It’s not heat—it’s trickery.
13. Why Do Onions Make You Cry?
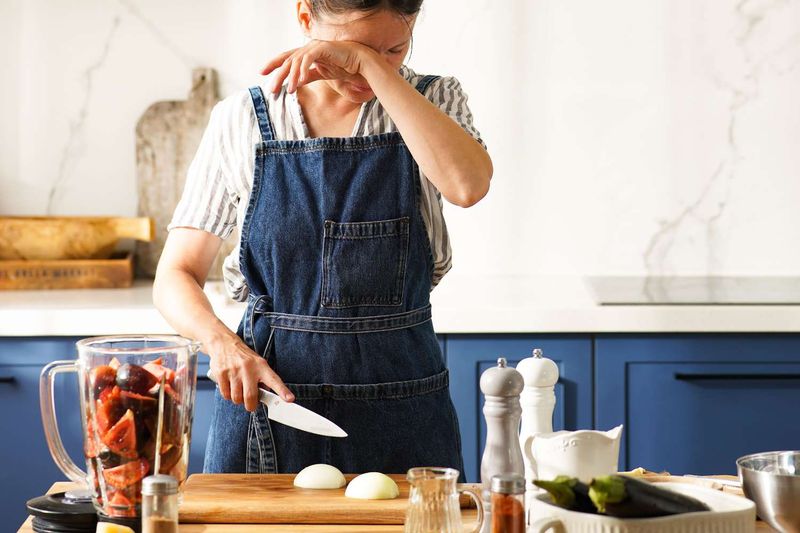

Onions contain sulfur compounds that turn into gas when you slice them. This gas reacts with the moisture in your eyes, forming sulfuric acid. Your body produces tears to flush the irritant away.
Cutting near the root releases the most gas, since it holds the highest concentration. Chilling the onion or cutting under running water can reduce the tears. It’s not drama—it’s chemistry.
14. Is Eating Raw Cookie Dough Really That Dangerous?
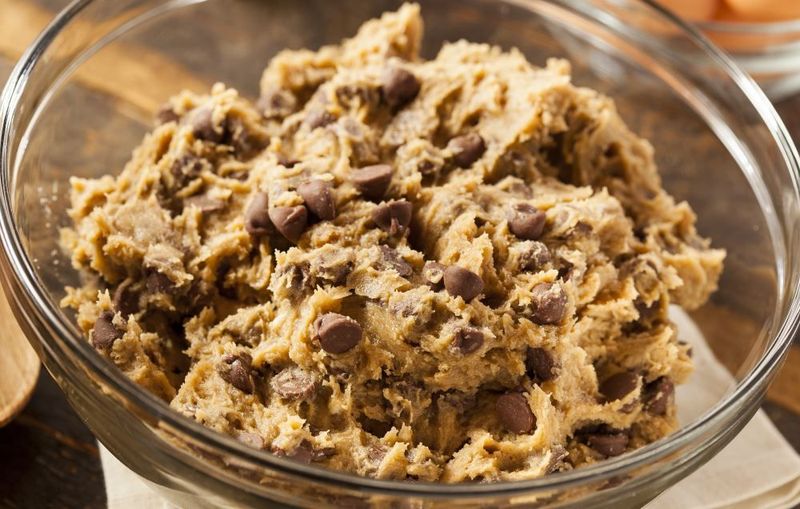

Raw eggs can carry salmonella, but that’s not the only risk. Raw flour also sometimes contains harmful bacteria like E. coli. Together, they make uncooked dough a possible source of food poisoning.
Edible doughs use pasteurized eggs or no egg at all and heat-treated flour. That makes them safer to eat by the spoonful. Tempting as it is, the raw batch carries real risk.
15. Why Do Crackers Have Little Holes In Them?
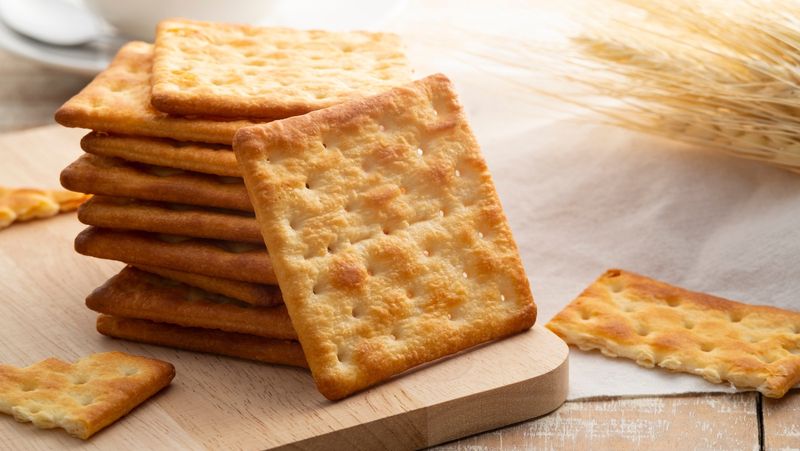

Those tiny holes serve a big purpose. They allow steam to escape during baking, which keeps the cracker flat and crisp. Without them, air pockets would form and create bubbles or uneven textures.
This technique is called docking and is essential in the cracker industry. It ensures uniformity, crunch, and proper structure. They’re tiny punctures with maximum importance.
16. What Exactly Is Spam Made Of?

Spam consists of pork shoulder, ham, salt, water, sugar, and sodium nitrite. The meat is ground and canned, then cooked inside the tin. Its texture is dense, salty, and slightly gelatinous from the natural fats.
It became a wartime staple due to its long shelf life and low cost. Though polarizing, it’s beloved in Hawaii, Korea, and parts of the American South. It’s culinary nostalgia in a can.
17. Why Does Some Ice Cream Freeze Harder Than Others?

Sugar lowers the freezing point of ice cream, keeping it scoopable. Less sugar or more air can make it rock solid. Premium brands often have less air and more fat, which adds richness but makes the product denser.
Your home freezer also affects texture—too cold, and even creamy ice cream becomes brittle. Ingredients, recipe, and storage all play a role. It’s frozen science with every pint.
18. Can You Survive On Potatoes Alone?

Potatoes are surprisingly complete, offering carbs, protein, fiber, and vitamin C. In theory, they could sustain you for a long time. But they lack essential nutrients like vitamin B12, calcium, and healthy fats.
Adding dairy, like milk or butter, improves the nutrient profile. Long-term survival isn’t ideal, but short-term? Definitely possible. The Irish famously came close.
19. What Makes Sour Candy So Sour?

Sour candy gets its tang from acids like citric, malic, or tartaric acid. These coat the candy surface and stimulate salivary glands instantly. Some candies even use acid crystals for an extra punch.
The sensation is sharp and brief, usually giving way to sweetness. The best sour candies balance shock with flavor. It’s edible electricity for the taste buds.
20. Is Orange Juice And Toothpaste The Worst Combo Ever?
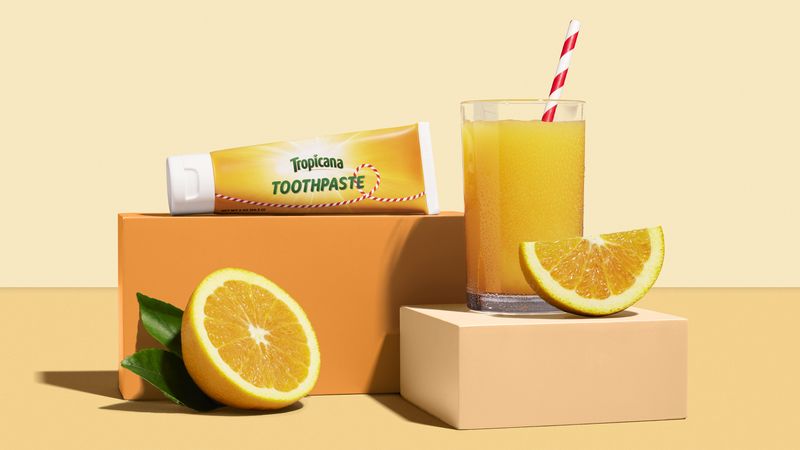

Toothpaste contains sodium lauryl sulfate, which dulls sweetness receptors. That makes orange juice taste bitter and metallic. Your mouth is chemically sabotaged by your own hygiene.
The clash is so intense, it’s almost legendary. Wait 30 minutes after brushing if you want your juice to taste normal. Breakfast harmony depends on timing.
